Main Page
Old things!
Radios
You will find a few notes here eventually!
TBA
Computing
General Notes
VMware remote support esxi
Useful command, working remotley
ESXi 4.x, 5.x and 6.0 To power on a virtual machine from the command line: <pre> List the inventory ID of the virtual machine with the command: vim-cmd vmsvc/getallvms |grep <vm name> Note: The first column of the output shows the vmid. Check the power state of the virtual machine with the command: vim-cmd vmsvc/power.getstate <vmid> Power-on the virtual machine with the command: vim-cmd vmsvc/power.on <vmid> Open a console session where the esxcli tool is available, either in the ESXi Shell, the vSphere Management Assistant (vMA), or the location where the vSphere Command-Line Interface (vCLI) is installed. Get a list of running virtual machines, identified by World ID, UUID, Display Name, and path to the .vmx configuration file by running this command: esxcli vm process list Power off one of the virtual machines from the list using this command: esxcli vm process kill --type= [soft,hard,force] --world-id= WorldNumber Notes: Three power-off methods are available. Soft is the most graceful, hard performs an immediate shutdown, and force should be used as a last resort. Alternate power off command syntax is: esxcli vm process kill -t [ soft,hard,force] -w WorldNumber Repeat Step 2 and validate that the virtual machine is no longer running. For ESXi 4.1: Get a list of running virtual machines, identified by World ID, UUID, Display Name, and path to the .vmx configuration file by running this command: esxcli vms vm list Power off one of the virtual machines from the list by running this command: esxcli vms vm kill --type= [soft,hard,force] --world-id= WorldNumber
Bind 9
Current ip's for Coopzone
Link for settings Name Server config
Tsig keys
Setting up secure updates using TSIG keys for BIND 9 for DNS agent
In the following example, the domain is example.com.
To use secure updates using TSIG keys, perform the following steps at the DNS server:
Run the dnssec-keygen command with the HMAC-MD5 option to generate a pair of files that contain the TSIG key:
# dnssec-keygen -a HMAC-MD5 -b 128 -n HOST example.com.
View the example.com.+157+00000.key file. After you run the cat command, the contents of the file resembles:
# cat example.com.+157+00000.key
example.com. IN KEY 512 3 157 +Cdjlkef9ZTSeixERZ433Q==
Copy the shared secret (the TSIG key), which looks like:
+Cdjlkef9ZTSeixERZ433Q==
Configure the DNS server to only allow TSIG updates using the generated key. Open the named.conf file and add these lines.
key example.com. {
algorithm hmac-md5;
secret "+Cdjlkef9ZTSeixERZ433Q==";
};
Where +Cdjlkef9ZTSeixERZ433Q== is the key.
In the named.conf file, edit the appropriate zone section and add the allow- updates sub-statement to reference the key:
allow-update { key example.com. ; } ;
Save and restart the named process.
You need both files to use nsupdate to your dns server.
Tsig Keys part 2 the easy way
The above method works, but the up-to-date versions of dnssec-keygen no longer supports HMAC. So you can still use above but with different key types. Really using dnssec-keygen is a bit overkill for tsig anyway.
This and the fact that the vast majority using t-sig are for simple dns updates, you can use this as an alternative:
- Generatethe config for bind9 and nsupdate in obe go with:
ddns-confgen -k update_key -z coopzone.uk.to
This will give an output you can save to a file and use as the key for nsupdate and you can add the same output to a bind zone file to allow the updates. It even gives you the instructions on how to use it!
Sample output:
ddns-confgen -k update_key -z coopzone.uk.to
# To activate this key, place the following in named.conf, and
# in a separate keyfile on the system or systems from which nsupdate
# will be run:
key "update_key" {
algorithm hmac-sha256;
secret "8jWVFokMGOIHgrqu35zhYg5zdjSQDCM+4f2dfSG+Vg8=";
};
# Then, in the "zone" definition statement for "coopzone.uk.to",
# place an "update-policy" statement like this one, adjusted as
# needed for your preferred permissions:
update-policy {
grant update_key zonesub ANY;
};
# After the keyfile has been placed, the following command will
# execute nsupdate using this key:
nsupdate -k <keyfile>
Using let's encrypt certificates
Plenty of info on how to use these from let's encrypt.
But if you want to use them on another service other than https. You can create a dummy website using apache/nginx. Then create the certificate and copy it to your server. The only stipulation being you must be on the same ip address.
In this example config, both vpn and www hosts are on one ip address, but different ports.
vpn=5000 www=80,443
# Settings for dummy server to get a cert for smtp
server {
listen 80;
root /var/www;
server_name vpn.coopzone.org.uk;
location /.well-known {
root /var/www/vpn/;
}
}
Create the dummy location:
mkdir -p /var/www/vpn/.well-known/acme-challenge
Use certbot to create the certificate:
certbot certonly --webroot -w /var/www/vpn/ -d vpn.coopzone.org.uk
Now copy the keys / certificates to the correct server or where ever your vpn lives. I do this in the same cronjob that updates the certificates using certbot reniew.
Linux
linux Linux (centos / debian) notes
SASL testing/setup
Setup on new server apt-get install libsasl2-2 sasl2-bin libsasl2-modules-db
change /etc/defaults/saslauthd lines:
START=yes MECHANISMS="sasldb" OPTIONS="-c -m /var/spool/postfix/var/run/saslauthd"
add sasl group to postfix user usermod -G sasl postfix
create /etc/postfix/sasl/smtpd.conf
pwcheck_method: saslauthd saslauthd_plugin: sasldb mech_list: PLAIN LOGIN
Need this section in master.cf
192.168.1.151:submission inet n - y - - smtpd -o smtpd_tls_security_level=encrypt -o smtpd_tls_received_header=yes -o smtpd_tls_auth_only=yes -o smtpd_tls_req_ccert=no -o smtpd_tls_cert_file=/etc/ssl/certs/cert -o smtpd_tls_key_file=/etc/ssl/private/cert.key -o smtpd_tls_CAfile=/etc/ssl/certs/QuoVardis.crt -o smtpd_sasl_type=cyrus -o smtpd_sasl_auth_enable=yes -o smtpd_sasl_path=smtpd -o smtpd_recipient_restrictions=permit_sasl_authenticated,reject -o smtpd_milters=inet:127.0.0.1:12345 -o smtpd_proxy_ehlo=smtp.host.com #
Adding/removing/showing authentication records
NOTE: You need to do these commands on all servers
commands to add/remove show users:
add user:
saslpasswd2 -c -u mail.mail.com derek
change user password:
saslpasswd2 -u mail.mail.com derek
del user:
saslpasswd2 -d -u mail.mail.com derek
list users:
sasldblistusers2
Testing
Test auth for sasl:
testsaslauthd -f /var/spool/postfix/var/run/saslauthd/mux -r mail.mail.com -u derek -p XXXXXXX
Test auth from postfix/smtpd using openssl
Generate an plain test password hash to test with
printf '\000derek@mail.mail.com\000XXXXXXXX' | openssl base64 -A
(copy the output ready to paste below)
Connect to the server to test the authentication.
openssl s_client -connect mail.mail.com:587 -starttls smtp
......
ehlo local
AUTH PLAIN {copy text from above}
235 2.7.0 Authentication successful
quit
221 2.0.0 Bye
Sasl Postfix relayhost problems
Settings should be:
smtp_sasl_auth_enable = yes smtp_sasl_password_maps = hash:/etc/postfix/sasl_passwd smtp_sasl_security_options = noanonymous #smtp_sasl_tls_security_options = noanonymous smtp_tls_security_level = encrypt header_size_limit = 4096000 relayhost = [the_relay]:587
sasl_password:
[the_relay]:587 saslrelay@auth.cz0.uk:verygoodpassword
Make sure you have cyrus client installed, or you will get NO MECH AVAILABLE
yum install cyrus-sasl-plain systemctl restart postfix
SoftEther VPN Notes
To diable vpnserver from calling home, i.e. stop all the chit-chat for nat traversal and just use it as a normal vpnserver.
Step 1 dissable DDNS
change the config file DDNS section to read:
declare DDnsClient { bool Disabled true }
Step 2 dissable UDP acceleration I did this from the config file by setting:
bool DisableUdpAcceleration true
Step 3, Disable Nat Traversal In the config file change the following setting.
bool DisableNatTraversal true
Step 4, turn off keep alive. This is via the GUI on the server encryption and network button.
Step 5, turn of auto update check. Again this is via the GUI on the server encryption and network button.
Having done the above (thanks to dnobori, for the ones I missed) and restarted the server, I know don't see any outbound / unexpected traffic.
Virtualization
Qcow2 images
/usr/bin/qemu-img create -f qcow2 -o preallocation=metadata /export/vmimgs/glacier.qcow2 8G
Qcow2 with LXC
You can use, qemu-nbd to mount a qcow image then copy/create the rootfs to it.
then if you use the following options in the config file:
lxc.hook.pre-start = /var/lib/lxc/up.sh lxc.hook.post-stop = /var/lib/lxc/down.sh
and make sure each config file has a unique nbd_device
#MUST set the nbd device to be unique for each container lxc.rootfs = /dev/nbd1
up.sh
#!/bin/bash
qemu-nbd -c ${LXC_ROOTFS_PATH} /lvmdir/${1}.qcow2
exit 0
down.sh
#!/bin/bash
while [ -f /sys/fs/cgroup/pids/lxc/${1}/pids.current ]; do
sleep 0.5
done
qemu-nbd -d ${LXC_ROOTFS_PATH}
exit 0
Brother 32bit drivers on 64bit linux
Debian example:
apt-get install lib32z1 lib32ncurses5 optional: apt-get install cups mkdir -p /var/spool/lpd dpkg -i --force-all mfc5890cnlpr-1.1.2-2a.i386.deb dpkg -i --force-all mfc5890cncupswrapper-1.1.2-2a.i386.deb
Some info for LVM
Using Snapshots.
Create a snapshot
lvcreate -L 1G -s -n test1_snap /dev/vg0/test1
(Make it big enough to take the changes you make)
To revert the snapshot (step back to before any changes)
1, umount it (stop using it) the LVM needs to be free for the revert to work
2, use:
lvconvert —merge /dev/vg0/test1_snap
3, The above will also remove the snapshot volume.
To commit the snapshot
1, unmount it (stop using it)
2, use:
lvremove -f /dev/vg0/test1_snap
Openvz / proxmox
Adding nat iptables modules to container, example:
vzctl set 115 --iptables "iptable_nat iptable_filter iptable_mangle ip_conntrack ipt_conntrack ipt_REDIRECT ipt_REJECT ipt_multiport ipt_helper ipt_LOG ipt_state" --save
virt All sorts on virtualization, Xen etc
Windows does not boot virtio especially after moving vm
1. Add both windows 10 DVD/CD ISO and virtio driver ISO to VM. Make a note of the drive letters assigned by windows (or once booted to recovery mode, you can manually dir each drive to find them) The latest driver ISO can be pulled out of the RPMs found at https://fedorapeople.org/groups/virt/virtio-win/repo/latest/
2. Boot off windows 10 DVD/CD and get into a command prompt from repair mode option.
3. Load the driver via the CLI e.g.
drvload e:\viostor\w10\amd64\viostor.inf
In my case e: was where the virtio install ISO got assigned.
4. After loading the driver f: was where the windows install became mounted.
5. Use the DISM command to inject the storage controller driver
dism /image:f:\ /add-driver /driver:e:\viostor\w10\amd64\viostor.inf
As above, change drive letter assignments according to your own environment.
KVM settings to help windows idle cpu issue
<clock offset='localtime'> <timer name='rtc' tickpolicy='catchup'/> <timer name='pit' tickpolicy='delay'/> <timer name='hpet' present='yes'/> <timer name='hypervclock' present='yes'/> </clock>
ABOVE: the hpet = yes line is the change, normally hpet = no.
Sometimes it's better like this (not all the "features" are needed, if virsh complains about them just remove the line)
It seems to be mostly the clock options that make a real difference to cpu idle 40% -> 1-2%
<features>
<acpi/>
<apic/>
<hyperv>
<relaxed state='on'/>
<vapic state='on'/>
<spinlocks state='on' retries='8191'/>
<synic state='on'/>
<stimer state='on'/>
</hyperv>
<vmport state='off'/>
</features>
<clock offset='localtime'>
<timer name='rtc' tickpolicy='catchup'/>
<timer name='pit' tickpolicy='delay'/>
<timer name='hpet' present='no'/>
<timer name='hypervclock' present='yes'/>
</clock>
Openvz7 virtuozzo
Either install in from the bare-hardware install CD, or if you only want to run it in a KVM/VMWARE environment do this:
Install basic Centos7 system. setup /vz as ext4
setup network
(you need bridge-utils)
update
(optional)
Next install the following:
yum install -y wget net-tools vim lvm2
yum install -y epel-release
yum install -y yum-plugin-priorities
rpm -ivh python-subprocess32-3.2.6-5.vz7.1.x86_64.rpm
rpm -ivh openvz-release-7.0.0-57.vz7.x86_64.rpm
yum install -y vzkernel
Now install the tools:
yum install -y crit criu libvzctl libvzevent openvz-docs pcompact ploop ploop-lib vcmmd virtuozzo-motd vzctl vzmigrate vzpkgenv410x64 vzpkgenv44 vzpkgenv44x64 vzpkgenv47 vzpkgenv47x64 vzpkgenvdebx64 vzpkgenvzypp49x64 vzprocps vzreport vzstat vztt vztt-lib
Optional: (you only seem to need this if you use the templates / updates provided by openvz team, i don't)
yum install -y prl-disp-service
reboot
You should now update (several times!) Since openvz7 -> virtuozzolinux upgrade. At some point it may well moan that it does not have a GPG key for the new packages. You should be able to find the key on there website, just search for VZLINUX_GPG_KEY.
Last time I did this install you can download and install it like this:
wget https://docs.virtuozzo.com/keys/VZLINUX_GPG_KEY mv VZLINUX_GPG_KEY /etc/pki/rpm-gpg/
Add any templates if you want to use the vzlinuz7 templates ( i don't as yet):
yum install -y `yum search x86_64-ez | grep noarch | awk '{print $1}’`
you need to update the local cache for each template installed, so for cento7 it would be:
vzpkg update cache centos-7-x86_64
(it's the same name as the templates installed above but without the -ez on the end!)
at this point it's more or less the same as the old openvz for cents 6, if you want to use the new tools for install etc then:
optional:
yum install -y prlctl
LXC
LXC Config in Azure VM
to setup host basic notes
Build ubuntu server 18
apt install iptables-persistent
add rule to snat any 10.x.x.x to the main ip on eth0
configure swap space /etc/waagent.conf
apt-get install zfsutils-linux lxc
Clam-AV or HAproxy
You can either install clamav on the host VM, as below, or if you have access to a central clamd scan engine (this is preferred as you only need one VM with enough memory to handle it, at least 2 gig) see using haproxy next section.
Clamav
apt-get install clamav-daemon
change /etc/clamav/clamd.conf
LocalSocket /var/run/clamav/clamd.ctl #FixStaleSocket true #LocalSocketGroup clamav #LocalSocketMode 666 TCPAddr 192.168.200.1 TCPSocket 3310
Haproxy
Install haproxy on the host VM
apt install haproxy
then configure a frontend/backend to connect port 3310 to clamd scanner hosts, example:
listen stats
bind 127.0.0.1:8404
stats enable
stats uri /stats
stats refresh 5s
frontend clamav
bind 192.168.200.1:3310
mode tcp
option tcplog
timeout client 300s
default_backend clamav_backend
#note: timeout client and server are the same as recommended for tcp connections
backend clamav_backend
mode tcp
timeout connect 30s
timeout server 300s
balance roundrobin
default-server inter 10s fall 2 rise 1
server clamav_mail2 ip-first:3310 check weight 100
server clamav_home ip-second:3310 check weight 10
Setup lxc bridge
change/create /etc/default/lxc-net
LXC_BRIDGE="lxcbr0" LXC_ADDR="192.168.200.1" LXC_NETMASK="255.255.255.0" LXC_NETWORK="192.168.200.0/24" LXC_DHCP_RANGE="192.168.200.128,192.168.200.253" LXC_DHCP_MAX="125" USE_LXC_BRIDGE="true"
create the disk file for LXC
dd if=/dev/zero of=/zdisk0_block bs=1024M count=26 zpool create zdisk0 /zdisk0_block zfs set compress=on zdisk0 zfs set dedup=on zdisk0
LXC using multiple ip's and iptables
The basic idea is to attach public ip's to additional ip's on the azure vm, then use iptables to re-direct traffic to LXC containers.
First you have to add multiple secondary static ip address's to your network card on the azure vm. This is not a full tutorial so you will have to work your way through the azure interface to find this for yourself.
NOTE : This breaks the waagent ! You must SNAT the traffic from the vm to appear as the primary ip address on the network card when appearing from the 10.0.0.0 ip's, then if you need to add addition SNAT rules for the secondary ip address's. If you don't do this waagent looses connectivity to the end points in azure and has a pink fit!
NOTE 2: No so critical, the other SNAT rules match outbound connections to the eventual public ip's, either one-to-one or many-to-one
NOTE 3: The last rule MASQUERADE is a catch all for any missing SNAT lines, it really should be another SNAT rule, but this one is actually added by LXC-NET so i just left it in place.
See example iptables, in this example (only showing the nat rules, azure adds others in using waagent) the last but one line:
-A POSTROUTING -s 10.0.0.0/24 -o eth0 -j SNAT --to-source 10.0.0.6
Is crtical to keeping waagent a happy bunny!
Example:
*nat :PREROUTING ACCEPT [0:0] :INPUT ACCEPT [0:0] :OUTPUT ACCEPT [8:480] :POSTROUTING ACCEPT [0:0] -A PREROUTING -d 10.0.0.40/32 -i eth0 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 53 -j DNAT --to-destination 192.168.200.10 -A PREROUTING -d 10.0.0.40/32 -i eth0 -p udp -m udp --dport 53 -j DNAT --to-destination 192.168.200.10 -A PREROUTING -d 10.0.0.40/32 -i eth0 -p tcp -m tcp --dport 22 -j DNAT --to-destination 192.168.200.10 -A PREROUTING -d 10.0.0.40/32 -i eth0 -p tcp -m multiport --dports 25,465,587,993 -j DNAT --to-destination 192.168.200.18 -A PREROUTING -d 10.0.0.43/32 -i eth0 -p tcp -m multiport --dports 443,80 -j DNAT --to-destination 192.168.200.13 -A PREROUTING -d 10.0.0.44/32 -i eth0 -p tcp -m multiport --dports 443,444,500,4500 -j DNAT --to-destination 192.168.200.17 -A PREROUTING -d 10.0.0.44/32 -i eth0 -p udp -m multiport --dports 5060,443,444,500,4500 -j DNAT --to-destination 192.168.200.17 -A PREROUTING -d 10.0.0.44/32 -i eth0 -p udp -m udp --dport 10000:20000 -j DNAT --to-destination 192.168.200.17 -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.200.10/32 ! -d 192.168.200.0/24 -j SNAT --to-source 10.0.0.40 -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.200.18/32 ! -d 192.168.200.0/24 -j SNAT --to-source 10.0.0.40 -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.200.13/32 ! -d 192.168.200.0/24 -j SNAT --to-source 10.0.0.43 -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.200.17/32 ! -d 192.168.200.0/24 -j SNAT --to-source 10.0.0.44 -A POSTROUTING -s 10.0.0.0/24 -o eth0 -j SNAT --to-source 10.0.0.6 -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.200.0/24 ! -d 192.168.200.0/24 -j MASQUERADE
LXC 2.0 on Centos 7
Install a base system for Centos 7 + whatever tools you normally use, vim, wget etc
search for and download the lxc 2.0 repo called "thm-lxc2.0-epel-7.repo", copy to your /etc/yum.repos.d
enable the epel repo, yum install epel-release
install:
yum install lxc lxc-templates
LXC 2.1 Build on Centos from source
yum -y groupinstall base development yum -y install libcap-devel yum -y install epel-release yum -y install iptables-services yum -y install docbook2X yum -y update yum clean all cd /usr/local/src wget https://linuxcontainers.org/downloads/lxc/lxc-2.1.0.tar.gz tar xvf lxc-2.1.0.tar.gz cd lxc-2.1.0/ ./configure --enable-capabilities --enable-doc --prefix=/usr --sysconfdir=/etc --localstatedir=/var make install
Set a different root / home directory for the lxc containers, if required:
cat /etc/lxc/lxc.conf lxc.lxcpath = /vm
Edit the file above to suite your needs
Next alter create the default file, for anything you want all containers to start with:
cat /etc/lxc/default.conf lxc.net.0.type = veth [root@lxc1 ~]# more /etc/lxc/default.conf lxc.net.0.type = veth lxc.net.0.link = br0 lxc.net.0.flags = up lxc.net.0.hwaddr = 00:16:3e:xx:xx:xx lxc.cgroup.memory.limit_in_bytes = 384000000 lxc.start.auto = 0
Now create an ld.so.con file to include the libraries for LXC
cat /etc/ld.so.conf.d/lxc.conf /usr/lib
And the default network settings
cat /etc/sysconfig/lxc-net LXC_BRIDGE="lxcbr0" USE_LXC_BRIDGE="true" LXC_ADDR="10.0.0.1" LXC_NETWORK="255.255.255.0" LXC_DHCP_RANGE="10.0.0.10,10.0.0.99"
LXC no console on container when using systemd
Create your own copy of the getty@.service cp /lib/systemd/system/getty@.service /etc/systemd/system Comment out the line ConditionPathExists=/dev/tty0 in the copied getty@.service
LXC apparmor settings for autofs, smb, nfs
In the file /etc/apparmor.d/lxc/lxc-default-cgns
change/add :
deny mount fstype=devpts, mount fstype=cgroup -> /sys/fs/cgroup/**, mount fstype=cgroup2 -> /sys/fs/cgroup/**, mount fstype=rpc_pipefs, mount fstype=nfs, mount fstype=cifs, mount fstype=autofs,
Mac OSX
mac Mac related notes
Vodaphone useful numbers
vodafone Vodafone numbers
Apps and software
- software Applications notes (mostly web based apps, notes on configuring building apache,php,openssl etc)
- unreal Unreal tournament
- bitsBits and pieces
- asterisk Asterisk notes
- mwiki MediaWiki bits and bobs
- dovecot Things about dovecot and postfix
- postfixadmin Adding new fields to postfix admin v3
- Docmgr Installation notes
DNS
DNS related Notes on dns, mostly out of date
Mac DNS Mac DNS flush cache
mariadb mysql replication Master/Master on Centos 7
On both servers, add entries for the hosts in /etc/hosts, in our case db1 and db2
Configure the firewall for mysql:
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=3306/tcp firewall-cmd --reload
On db1, in /etc/my.cnf.d/server.cnf
[mariadb-5.5] # bind-address = 127.0.0.1 server-id = 2 report_host = db2 log_bin = /var/log/mariadb/mariadb-bin log_bin_index = /var/log/mariadb/mariadb-bin.index relay_log = /var/log/mariadb/relay-bin relay_log_index = /var/log/mariadb/relay-bin.index auto_increment_increment = 2 auto_increment_offset = 2 # replicate-do-db = testdb expire_logs_days = 14
On db2, in /etc/my.cnf.d/server.cnf
[mariadb-5.5] # bind-address = 127.0.0.1 server-id = 1 report_host = db1 log_bin = /var/log/mariadb/mariadb-bin log_bin_index = /var/log/mariadb/mariadb-bin.index relay_log = /var/log/mariadb/relay-bin relay_log_index = /var/log/mariadb/relay-bin.index auto_increment_increment = 2 auto_increment_offset = 1 # replicate-do-db = testdb expire_logs_days = 14
On both db1 and db2
restart mariadb on both servers
systemctl restart mariadb systemctl status mariadb
Connect to the sql server.
mysql -uroot -p
Create the replication user
create user 'replusr'@'%' identified by 'xxx-verystrongpassword-xxx'; grant replication slave on *.* to 'replusr'@'%';
On db1, make note of master status;
show master status;
show master status; +--------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+ | File | Position | Binlog_Do_DB | Binlog_Ignore_DB | +--------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+ | mariadb-bin.000001 | 479 | | | +--------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
On db2, configure the slave/master setup
STOP SLAVE; CHANGE MASTER TO MASTER_HOST='db1', MASTER_USER='replusr', MASTER_PASSWORD='xxx-verystrongpassword-xxx', MASTER_LOG_FILE='mariadb-bin.000001', MASTER_LOG_POS=479; START SLAVE;
show the slave status (look for any errors)
SHOW SLAVE STATUS\G
Make a note of the master status:
show master status; +--------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+ | File | Position | Binlog_Do_DB | Binlog_Ignore_DB | +--------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+ | mariadb-bin.000002 | 245 | | | +--------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
On db1. setup slave/master (as on the other server but other direction)
STOP SLAVE; CHANGE MASTER TO MASTER_HOST='db2', MASTER_USER='replusr', MASTER_PASSWORD='xxx-verystrongpassword-xxx', MASTER_LOG_FILE='mariadb-bin.000002', MASTER_LOG_POS=245; START SLAVE;
Check status of slave, again look for errors.
SHOW SLAVE STATUS\G
Thats it, you can also check the master status:
SHOW MASTER STATUS\G
You should be able to create a database on one and it will appear on the other etc.
Rebuild Database Master - Master
If your MySQL (5.0+) replication is broken, there’s two ways to fix it: The easy way, and the right way.
Run commands starting with $ on Unix.
Run commands starting with mysql> in the MySQL client.
The easy way: Skip the problem
If you hit both databases at the same time, with the same INSERT, they will create their own record, and try and replicate to the other, which already has that record, causing a duplicate error.
In a simple case like that, you just want to skip the offending statement:
mysql>SET GLOBAL SQL_SLAVE_SKIP_COUNTER=1; START SLAVE;
More details on skipping MySQL duplicate errors
Most of the time, you skip one statement, and replication breaks again straight away, because there’s a whole queue of problem statements coming up.
The right way: Rebuild
If you are not sure that you can skip the duplicate, or if replication has been broken long enough that your two servers are out of synch, pick one database to be the master, and rebuild the other from a copy of that master.
First make sure your site is only using the master server. Stop any processes that might modify data on the server you need to rebuild.
We have two database servers:
Good Server: The good one, with the correct data.
Rebuilding Server: The one we are fixing. All it’s data will be erased with the Good Server data.
1. On the Good Server
Dump data from the Good Server. The master-data switch adds a statement at the end of the file to start replication.
The quick switch makes dumping large tables use a lot less memory, so on a VPS it’s much faster.
All tables will locked during the dump.
Replace ‘my_database’ with your database name.
$ mysqldump --add-drop-table --master-data --routines
--quick -u root -p my_database > my_database.sql
$ bzip2 my_database.sql
2. On the Rebuilding Server
Copy the dump onto the Rebuilding Server. Replace ‘myuser’, ‘good-server’ and ‘my_database’ as appropriate.
$ scp myuser@good-server:my_database.sql.bz2 . $ bunzip my_database.sql
Load the dump. This can take a few minutes for a large database.
mysql> stop slave; $ mysql -u root -p my_database < my_database.sql
mysql> show slave status\G
You should see Slave_IO_Running: Yes and Slave_SQL_Running: Yes.
The master-data switch to mysqldump, in step 1, started replication at the right place for us. How nice. I love MySQL.
The \G means show vertical instead of the usual horizontal. It works with any MySQL command.
Now you have statements flowing Good Server –> Rebuilding Server. Next we need to get data going the other way.
mysql> flush tables with read lock; mysql> show master status;
Make a note of the File and Position rows.
3. On the Good Server
Set the slave here to be in synch with Rebuilding Server. Use the file name and log position from the previous step.
mysql> stop slave; mysql> change master to master_log_file='mysql-bin.000044', master_log_pos=132059667; mysql> start slave; mysql> show slave status\G
4. On the Rebuilding Server
mysql> unlock tables;
Windows
To enable telnet
Start
Control Panel
Programs And Features
Turn Windows features on or off
Check Telnet Client
Windows product keys (copied from Microsoft web site)
MSProductKeys Microsoft keys for use with corporate products
How to Convert Evaluation Server 2016 or 2019 to Licensed Version
To convert Windows Server 2019 or 2016 Evaluation to Licensed (Retail):
Open PowerShell as Administrator and give the following command to find the installed version of Server 2016/19:
DISM /Online /Get-CurrentEdition
Then give the following command to convert the Server 2016 Evaluation version to Full Retail (Licensed):
DISM /online /Set-Edition:ServerEdition /ProductKey:XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX /AcceptEula
For example… If the installed edition is the "ServerStandarEval" then the command is:
DISM /online /Set-Edition:ServerStandard /ProductKey:XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX /AcceptEula
If the installed edition is the "ServerDatacenterEval" then the command is:
DISM /Online /Set-Edition:ServerDatacenter /ProductKey:xxxxx-xxxxx-xxxxx-xxxxx-xxxxx /AcceptEula
If you have a KMS host running in your deployment, then you can use a KMS Product key for activation or you can use the KMS key to convert the Evaluation version to licensed and then (after the conversion), to change the product key and activate Windows by using the slmgr.vbs /ipk command.
Using Rsync for backup
First you need to install Cygwin, with the ssh client and rsync client.
Here is a useful bat file to rsync some directories back to your ssh server.
@echo off set user=cooperd cd c:/Users/%user% for %%F in ( Documents Desktop ) do ( echo %%F %1 rsync -avz %1 -e "ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no -o UserKnownHostsFile=/dev/null -i c:/Users/%user%/.ssh/backup_key -2 -p022"^ %%F xxxx@yyyy.com:/data/backup/windows/%user%/ )
Adjust the username as required. Also the username for the ssh server, the server and possible the -p022 to specify the ssh port
Building Windows to go notes
partition disk.
Command Prompt with administrative rights
diskpart, (if you have already used the drive letters suggested below choose a different one and substitute it in the commands.)
List the available disks by running "list disk" and you should see your usb device.
Select your USB drive by typing "select disk #" and hit Enter. For example, “select disk 1”.
Clean the partitions on the disk by typing "clean" and hit Enter.
Now create the boot partition by running the following command:
create partition primary size=350 Now create the OS partition by running the following command to create a partition taking up all remaining space: create partition primary The boot partition needs to be formatted, configured and assigned a drive letter, run the following commands: select partition 1 format fs=fat32 quick active assign letter=b (if the b drive letter is already in use on your PC, substitute a different letter and replace b with your letter throughout the rest of this guide) The same must be done for the OS partition, run the following different commands: select partition 2 format fs=ntfs quick assign letter=o (if the o drive letter is already in use on your PC, substitute a different letter and replace o with your letter throughout the rest of this guide) Exit Diskpart by typing Exit.
Extract wim file.
(from the windows 8/8.1 install media) sources directory.
dism /apply-image /imagefile:c:\path\install.wim /index:1 /applydir:o:\
add drivers (optional)
dism /image:u:\ /add-driver /driver:*BootCamp Directory*\Drivers /recurse
make bootable
o:\windows\system32\bcdboot o:\windows /f ALL /s b:
Revert windows 10 VPN connection to older type 'connect' button
Open regedit (WIN+R and type regedit.exe)
Go to
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\ControlPanel\Settings\Network
Take ownership of the “Network” key/folder (rightclick, Permissions)
Select “Advanced” in the Permissions window In the Advanced window,
select “Change” where the owner field is (top of the window)
Type in your username and save your changes. Close the advanced window.
Now select “Administrators” in the security tab. Make sure “Full control” is selected, then apply changes.
Now that’s done, double click “ReplaceVan” Change it’s value to 2
Certificates
Check key / cert are mached (also csr )
checking the modulus and the public exponent portions in the key and the Certificate must match.
But since the public exponent is usually 65537 and it's bothering comparing long modulus you can use the following approach:
$ openssl x509 -noout -modulus -in server.crt | openssl md5 $ openssl rsa -noout -modulus -in server.key | openssl md5
And then compare these really shorter numbers.
if I want to check to which key or certificate a particular CSR belongs you can compute
$ openssl req -noout -modulus -in server.csr | openssl md5
Re-install Grub / fix partitions
Boot from the live CD or live USB, in "Try Ubuntu" mode.
Determine the partition number of your main partition. GParted (which should already be installed, by default, on the live session) can help you here. I'm going to assume in this answer that it's /dev/sda2, but make sure you use the correct partition number for your system!
Mount your partition:
sudo mount /dev/sda2 /mnt #Replace sda2 with your partition number Bind mount some other necessary stuff:
for i in /sys /proc /run /dev; do sudo mount --bind "$i" "/mnt$i"; done
chroot into your Ubuntu install:
sudo chroot /mnt At this point, you're in your install, not the live session, and running as root. Update grub:
Remember to use blkid to get the UUID's for changing in the fstab before re-installing grub.
update-grub If you get errors, go to step 7. (Otherwise, it is optional.)
Re-install grub on new disk etc - alternative version
Terminal Commands
Mount the partition your Ubuntu Installation is on. If you are not sure which it is, launch GParted (included in the Live CD) and find out. It is usually a EXT4 Partition. Replace the XY with the drive letter, and partition number, for example: sudo mount /dev/sda1 /mnt.
mount /dev/sdXY /mnt
Now bind the directories that grub needs access to to detect other operating systems, like so.
mount --bind /dev /mnt/dev && mount --bind /dev/pts /mnt/dev/pts && mount --bind /proc /mnt/proc && mount --bind /sys /mnt/sys
Now we jump into that using chroot.
chroot /mnt
Now install, check, and update grub. This time you only need to add the drive letter (usually a) to replace X, for example: grub-install /dev/sda, grub-install –recheck /dev/sda.
grub-install /dev/sdX grub-install --recheck /dev/sdX
Remember to use blkid to get the UUID's for changing in the fstab before re-installing grub.
blkid /dev/sXX1 (root partion, etc) >> /etc/fstab
Once you have all the id's edit the fstab file and replace the old id's with the ones now at the end of the file from above commands. Clean up and save the file
Then re-build the grub menu
update-grub --recheck /dev/sXX (disk to use)
Now grub is back, all that is left is to exit the chrooted system and unmount everything.
umount /mnt/sys && umount /mnt/proc && umount /mnt/dev/pts && umount /mnt/dev &&
Shut down and turn your computer back on, and you will be met with the default Grub2 screen.
You may want to update grub or re-install burg however you like it.
Electronics Related
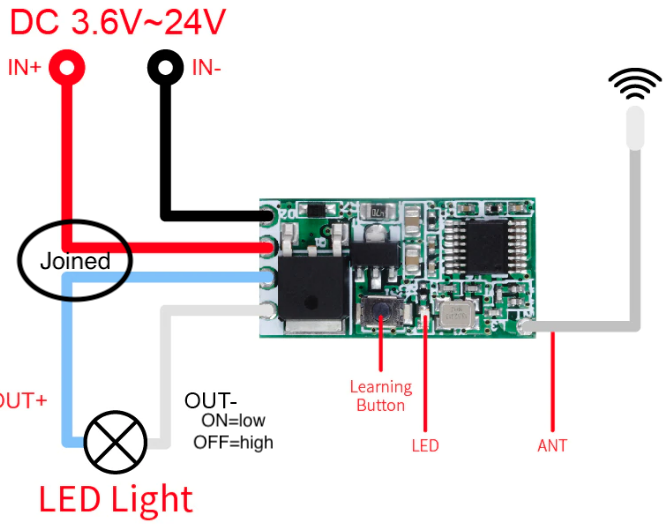
433mhz 1ch radio module
mini rf module
press 8 times to delete any codes (that would be the learning button!)
press 1 time for momentary use, then send a code
press 2 times for toggle, then send code.
press 3 time for latch mode, then send first code(on) followed by second code(off)
You need to delete codes to change modes(8 presses). Codes from 28280 upwards seem to work ok.
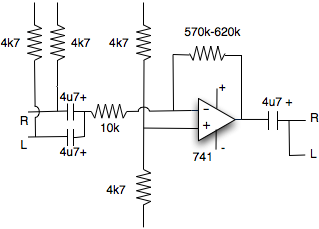
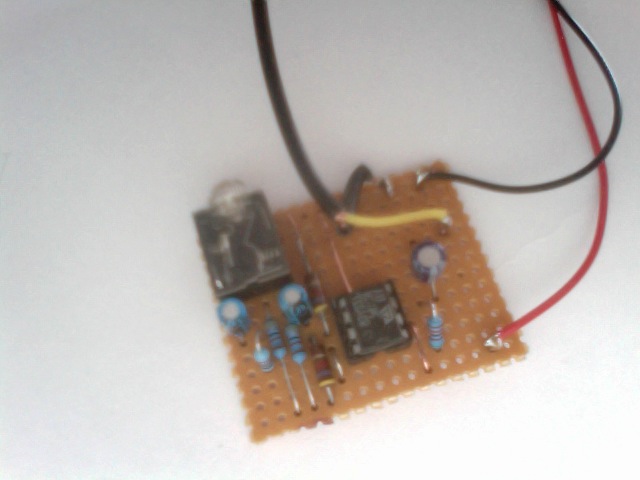
Microphone pre-amp for apple mac
This simple circuit was built on vero board in a matter of 40 mins. Not pretty but it was made of mostly second hand bits, infact two of the resistors bellow where from a PC board from a 1980's computer!
Arduino Atmega8 using internal 8mhz clock
How to add atmiga8 chip to the IDE interface for Arduino, this is for the old version 1.0.6. I've never bothered using the later versions but I would think is mostly the same
Change to the optiboot directory (this is on the Mac OS X version, for windows just look for the bootloaders directory
cd /Applications/Arduino.app/Contents/Resources/Java/hardware/arduino/bootloaders/optiboot/
Add this to the Makefile, I would suggest just after the existing atemga8 section, I used the letter i to indicate internal clock
atmega8i: TARGET = atmega8 atmega8i: MCU_TARGET = atmega8 atmega8i: CFLAGS += '-DLED_START_FLASHES=3' '-DBAUD_RATE=38400' atmega8i: LDSECTIONS = -Wl,--section-start=.text=0x1e00 -Wl,--section-start=.version=0x1ffe atmega8i: AVR_FREQ = 8000000L atmega8i: $(PROGRAM)_atmega8i.hex atmega8i: $(PROGRAM)_atmega8i.lst atmega8i_isp: atmega8i atmega8i_isp: TARGET = atmega8 # 2.7V brownout atmega8i_isp: HFUSE = CC # internal clock 8mhz atmega8i_isp: LFUSE = A4 # 512 byte boot atmega8i_isp: EFUSE = 04 atmega8i_isp: isp
You can then make the boot loader with the omake command (on the Mac you have to chmod +x omake first)
./omake atmega8i
(you will end up with a " optiboot_atmega8i.hex ") file in the directory,
Next add these lines to the boards.txt file (normally at the bottom of the file)
This adds two entries to your board selection the first 8-16MHZ is for Crystal clock, the second (8mhz) is the internal clock version at 8mhz. You can change the fuse bits to get other clock speeds if you need them.
############################################################## opti8.name=Arduino Optiboot-Atmega8-16 opti8.upload.protocol=arduino opti8.upload.maximum_size=7680 opti8.upload.speed=115200 opti8.bootloader.low_fuses=0xbf opti8.bootloader.high_fuses=0xcc opti8.bootloader.path=optiboot #opti8.bootloader.file=optiboot_atmega8-16.hex opti8.bootloader.file=optiboot_atmega8.hex opti8.bootloader.unlock_bits=0x3F opti8.bootloader.lock_bits=0x0F opti8.build.mcu=atmega8 opti8.build.f_cpu=16000000L opti8.build.core=arduino opti8.build.variant=standard ############################################################## ############################################################## opti8i.name=Arduino Optiboot-Atmega8-16 (8mhz) opti8i.upload.protocol=arduino opti8i.upload.maximum_size=7680 opti8i.upload.speed=38400 opti8i.bootloader.low_fuses=0xa4 opti8i.bootloader.high_fuses=0xcc opti8i.bootloader.path=optiboot opti8i.bootloader.file=optiboot_atmega8i.hex opti8i.bootloader.unlock_bits=0x3F opti8i.bootloader.lock_bits=0x0F opti8i.build.mcu=atmega8 opti8i.build.f_cpu=8000000L opti8i.build.core=arduino opti8i.build.variant=standard ##############################################################
Arduino Atmega328 using internal 8mhz clock
How to add atmiga328 chip to the IDE interface for Arduino, this is for the old version 1.0.6. I've never bothered using the later versions but I would think is mostly the same
Change to the optiboot directory (this is on the Mac OS X version, for windows just look for the bootloaders directory
# Standard atmega328, using 8Mhz internal RC oscillator # atmega328i: TARGET = atmega328 atmega328i: MCU_TARGET = atmega328p atmega328i: CFLAGS += '-DLED_START_FLASHES=3' '-DBAUD_RATE=38400' atmega328i: AVR_FREQ = 8000000L atmega328i: LDSECTIONS = -Wl,--section-start=.text=0x7e00 -Wl,--section-start=.version=0x7ffe atmega328i: $(PROGRAM)_atmega328i.hex atmega328i: $(PROGRAM)_atmega328i.lst atmega328i_isp: atmega328 atmega328i_isp: TARGET = atmega328 atmega328i_isp: MCU_TARGET = atmega328p # 512 byte boot, SPIEN atmega328i_isp: HFUSE = DE # Int. RC Osc. 8MHz, slowly rising power-65ms atmega328i_isp: LFUSE = E2 # 2.7V brownout atmega328i_isp: EFUSE = 05 atmega328i_8_isp: isp
You can then make the boot loader with the omake command (on the Mac you have to chmod +x omake first) ./omake atmega328i (you will end up with a " optiboot_atmega328i.hex ") file in the directory, Next add these lines to the boards.txt file (normally at the bottom of the file) This adds an entry to your board selection,"ATmega328 Optiboot 8MHz Int. RC Osc.". You can change the fuse bits to get other clock speeds if you need them.
############################################################## atmega328i.name=ATmega328 Optiboot 8MHz Int. RC Osc. atmega328i.upload.protocol=arduino atmega328i.upload.maximum_size=30720 atmega328i.upload.speed=38400 atmega328i.bootloader.low_fuses=0xE2 atmega328i.bootloader.high_fuses=0xDE atmega328i.bootloader.extended_fuses=0x05 atmega328i.bootloader.path=optiboot atmega328i.bootloader.file=optiboot_atmega328i.hex atmega328i.bootloader.unlock_bits=0x3F atmega328i.bootloader.lock_bits=0x0F atmega328i.build.mcu=atmega328p atmega328i.build.f_cpu=8000000L atmega328i.build.core=arduino atmega328i.build.variant=standard ##############################################################