Main Page
Main Page
VMware remote support esxi
Useful command, working remotley
ESXi 4.x, 5.x and 6.0 To power on a virtual machine from the command line: <pre> List the inventory ID of the virtual machine with the command: vim-cmd vmsvc/getallvms |grep <vm name> Note: The first column of the output shows the vmid. Check the power state of the virtual machine with the command: vim-cmd vmsvc/power.getstate <vmid> Power-on the virtual machine with the command: vim-cmd vmsvc/power.on <vmid> Open a console session where the esxcli tool is available, either in the ESXi Shell, the vSphere Management Assistant (vMA), or the location where the vSphere Command-Line Interface (vCLI) is installed. Get a list of running virtual machines, identified by World ID, UUID, Display Name, and path to the .vmx configuration file by running this command: esxcli vm process list Power off one of the virtual machines from the list using this command: esxcli vm process kill --type= [soft,hard,force] --world-id= WorldNumber Notes: Three power-off methods are available. Soft is the most graceful, hard performs an immediate shutdown, and force should be used as a last resort. Alternate power off command syntax is: esxcli vm process kill -t [ soft,hard,force] -w WorldNumber Repeat Step 2 and validate that the virtual machine is no longer running. For ESXi 4.1: Get a list of running virtual machines, identified by World ID, UUID, Display Name, and path to the .vmx configuration file by running this command: esxcli vms vm list Power off one of the virtual machines from the list by running this command: esxcli vms vm kill --type= [soft,hard,force] --world-id= WorldNumber
Using let's encrypt certificates
Plenty of info on how to use these from let's encrypt.
But if you want to use them on another service other than https. You can create a dummy website using apache/nginx. Then create the certificate and copy it to your server. The only stipulation being you must be on the same ip address.
In this example config, both vpn and www hosts are on one ip address, but different ports.
vpn=5000 www=80,443
# Settings for dummy server to get a cert for smtp
server {
listen 80;
root /var/www;
server_name vpn.coopzone.org.uk;
location /.well-known {
root /var/www/vpn/;
}
}
Create the dummy location:
mkdir -p /var/www/vpn/.well-known/acme-challenge
Use certbot to create the certificate:
certbot certonly --webroot -w /var/www/vpn/ -d vpn.coopzone.org.uk
Now copy the keys / certificates to the correct server or where ever your vpn lives. I do this in the same cronjob that updates the certificates using certbot reniew.
Linux
linux Linux (centos / debian) notes
SoftEther VPN Notes
To diable vpnserver from calling home, i.e. stop all the chit-chat for nat traversal and just use it as a normal vpnserver.
Step 1 dissable DDNS
change the config file DDNS section to read:
declare DDnsClient { bool Disabled true }
Step 2 dissable UDP acceleration I did this from the config file by setting:
bool DisableUdpAcceleration true
Step 3, Disable Nat Traversal In the config file change the following setting.
bool DisableNatTraversal true
Step 4, turn off keep alive. This is via the GUI on the server encryption and network button.
Step 5, turn of auto update check. Again this is via the GUI on the server encryption and network button.
Having done the above (thanks to dnobori, for the ones I missed) and restarted the server, I know don't see any outbound / unexpected traffic.
Virtualization
Qcow2 images
/usr/bin/qemu-img create -f qcow2 -o preallocation=metadata /export/vmimgs/glacier.qcow2 8G
Qcow2 with LXC
You can use, qemu-nbd to mount a qcow image then copy/create the rootfs to it.
then if you use the following options in the config file:
lxc.hook.pre-start = /var/lib/lxc/up.sh lxc.hook.post-stop = /var/lib/lxc/down.sh
and make sure each config file has a unique nbd_device
#MUST set the nbd device to be unique for each container lxc.rootfs = /dev/nbd1
up.sh
#!/bin/bash
qemu-nbd -c ${LXC_ROOTFS_PATH} /lvmdir/${1}.qcow2
exit 0
down.sh
#!/bin/bash
while [ -f /sys/fs/cgroup/pids/lxc/${1}/pids.current ]; do
sleep 0.5
done
qemu-nbd -d ${LXC_ROOTFS_PATH}
exit 0
Brother 32bit drivers on 64bit linux
Debian example:
apt-get install lib32z1 lib32ncurses5 optional: apt-get install cups mkdir -p /var/spool/lpd dpkg -i --force-all mfc5890cnlpr-1.1.2-2a.i386.deb dpkg -i --force-all mfc5890cncupswrapper-1.1.2-2a.i386.deb
Openvz / proxmox
Adding nat iptables modules to container, example:
vzctl set 115 --iptables "iptable_nat iptable_filter iptable_mangle ip_conntrack ipt_conntrack ipt_REDIRECT ipt_REJECT ipt_multiport ipt_helper ipt_LOG ipt_state" --save
virt All sorts on virtualization, Xen etc
Openvz7 virtuozzo
Either install in from the bare-hardware install CD, or if you only want to run it in a KVM/VMWARE environment do this:
Install basic Centos7 system. setup /vz as ext4
setup network
(you need bridge-utils)
update
(optional)
Next install the following:
yum install -y wget net-tools vim lvm2
yum install -y epel-release
yum install -y yum-plugin-priorities
rpm -ivh python-subprocess32-3.2.6-5.vz7.1.x86_64.rpm
rpm -ivh openvz-release-7.0.0-57.vz7.x86_64.rpm
yum install -y vzkernel
Now install the tools:
yum install -y crit criu libvzctl libvzevent openvz-docs pcompact ploop ploop-lib vcmmd virtuozzo-motd vzctl vzmigrate vzpkgenv410x64 vzpkgenv44 vzpkgenv44x64 vzpkgenv47 vzpkgenv47x64 vzpkgenvdebx64 vzpkgenvzypp49x64 vzprocps vzreport vzstat vztt vztt-lib
Optional: (you only seem to need this if you use the templates / updates provided by openvz team, i don't)
yum install -y prl-disp-service
reboot
all templates: yum install -y `yum search x86_64-ez | grep noarch | awk '{print $1}’`
you need to update the local cache for each template installed, so for cento7 it would be:
vzpkg update cache centos-7-x86_64
(it's the same name as the templates installed above but without the -ez on the end!)
at this point it's more or less the same as the old openvz for cents 6, if you want to use the new tools for install etc then:
optional:
yum install -y prlctl
LXC 2.0 on Centos 7
Install a base system for Centos 7 + whatever tools you normally use, vim, wget etc
search for and download the lxc 2.0 repo called "thm-lxc2.0-epel-7.repo", copy to your /etc/yum.repos.d
enable the peel repo, yum install epel-release
install:
yum install lxc lxc-templates
Mac OSX
mac Mac related notes
Vodaphone useful numbers
vodafone Vodafone numbers
Apps and software
- software Applications notes (mostly web based apps, notes on configuring building apache,php,openssl etc)
- unreal Unreal tournament
- bitsBits and pieces
- asterisk Asterisk notes
- mwiki MediaWiki bits and bobs
- dovecot Things about dovecot and postfix
- Docmgr Installation notes
DNS
DNS related Notes on dns, mostly out of date
Mac DNS Mac DNS flush cache
mariadb mysql replication Master/Master on Centos 7
On both servers, add entries for the hosts in /etc/hosts, in our case db1 and db2
Configure the firewall for mysql:
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=3306/tcp firewall-cmd --reload
On db1, in /etc/my.cnf.d/server.cnf
[mariadb-5.5] # bind-address = 127.0.0.1 server-id = 2 report_host = db2 log_bin = /var/log/mariadb/mariadb-bin log_bin_index = /var/log/mariadb/mariadb-bin.index relay_log = /var/log/mariadb/relay-bin relay_log_index = /var/log/mariadb/relay-bin.index auto_increment_increment = 2 auto_increment_offset = 2 # replicate-do-db = testdb
On db2, in /etc/my.cnf.d/server.cnf
[mariadb-5.5] # bind-address = 127.0.0.1 server-id = 1 report_host = db1 log_bin = /var/log/mariadb/mariadb-bin log_bin_index = /var/log/mariadb/mariadb-bin.index relay_log = /var/log/mariadb/relay-bin relay_log_index = /var/log/mariadb/relay-bin.index auto_increment_increment = 2 auto_increment_offset = 1 # replicate-do-db = testdb
On both db1 and db2
restart mariadb on both servers
systemctl restart mariadb systemctl status mariadb
Connect to the sql server.
mysql -uroot -p
Create the replication user
create user 'replusr'@'%' identified by 'xxx-verystrongpassword-xxx'; grant replication slave on *.* to 'replusr'@'%';
On db1, make note of master status;
show master status;
show master status; +--------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+ | File | Position | Binlog_Do_DB | Binlog_Ignore_DB | +--------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+ | mariadb-bin.000001 | 479 | | | +--------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
On db2, configure the slave/master setup
STOP SLAVE; CHANGE MASTER TO MASTER_HOST='db1', MASTER_USER='replusr', MASTER_PASSWORD='xxx-verystrongpassword-xxx', MASTER_LOG_FILE='mariadb-bin.000001', MASTER_LOG_POS=479; START SLAVE;
show the slave status (look for any errors)
SHOW SLAVE STATUS\G
Make a note of the master status:
show master status; +--------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+ | File | Position | Binlog_Do_DB | Binlog_Ignore_DB | +--------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+ | mariadb-bin.000002 | 245 | | | +--------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
On db1. setup slave/master (as on the other server but other direction)
STOP SLAVE; CHANGE MASTER TO MASTER_HOST='db2', MASTER_USER='replusr', MASTER_PASSWORD='xxx-verystrongpassword-xxx', MASTER_LOG_FILE='mariadb-bin.000002', MASTER_LOG_POS=245; START SLAVE;
Check status of slave, again look for errors.
SHOW SLAVE STATUS\G
Thats it, you can also check the master status:
SHOW MASTER STATUS\G
You should be able to create a database on one and it will appear on the other etc.
Windows
To enable telnet
Start
Control Panel
Programs And Features
Turn Windows features on or off
Check Telnet Client
Using Rsync for backup
First you need to install Cygwin, with the ssh client and rsync client.
Here is a useful bat file to rsync some directories back to your ssh server.
@echo off set user=cooperd cd c:/Users/%user% for %%F in ( Documents Desktop ) do ( echo %%F %1 rsync -avz %1 -e "ssh -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no -o UserKnownHostsFile=/dev/null -i c:/Users/%user%/.ssh/backup_key -2 -p022"^ %%F xxxx@yyyy.com:/data/backup/windows/%user%/ )
Adjust the username as required. Also the username for the ssh server, the server and possible the -p022 to specify the ssh port
Building Windows to go notes
partition disk.
Command Prompt with administrative rights
diskpart, (if you have already used the drive letters suggested below choose a different one and substitute it in the commands.)
List the available disks by running "list disk" and you should see your usb device.
Select your USB drive by typing "select disk #" and hit Enter. For example, “select disk 1”.
Clean the partitions on the disk by typing "clean" and hit Enter.
Now create the boot partition by running the following command:
create partition primary size=350 Now create the OS partition by running the following command to create a partition taking up all remaining space: create partition primary The boot partition needs to be formatted, configured and assigned a drive letter, run the following commands: select partition 1 format fs=fat32 quick active assign letter=b (if the b drive letter is already in use on your PC, substitute a different letter and replace b with your letter throughout the rest of this guide) The same must be done for the OS partition, run the following different commands: select partition 2 format fs=ntfs quick assign letter=o (if the o drive letter is already in use on your PC, substitute a different letter and replace o with your letter throughout the rest of this guide) Exit Diskpart by typing Exit.
Extract wim file.
(from the windows 8/8.1 install media) sources directory.
dism /apply-image /imagefile:c:\path\install.wim /index:1 /applydir:o:\
add drivers (optional)
dism /image:u:\ /add-driver /driver:*BootCamp Directory*\Drivers /recurse
make bootable
o:\windows\system32\bcdboot o:\windows /f ALL /s b:
Product keys from Microsoft's web site
NOTE: these keys are on Microsoft's website, they are Volume Licence KMS the keys and will not work with any other setup. They are reproduced here for convenience of having the keys in one place.
office: Office Professional Plus 2010 VYBBJ-TRJPB-QFQRF-QFT4D-H3GVB Office Standard 2010 V7QKV-4XVVR-XYV4D-F7DFM-8R6BM Office 2013 Professional Plus YC7DK-G2NP3-2QQC3-J6H88-GVGXT Office 2013 Standard KBKQT-2NMXY-JJWGP-M62JB-92CD4 Project 2013 Professional FN8TT-7WMH6-2D4X9-M337T-2342K Project 2013 Standard 6NTH3-CW976-3G3Y2-JK3TX-8QHTT Visio 2013 Professional C2FG9-N6J68-H8BTJ-BW3QX-RM3B3 Visio 2013 Standard J484Y-4NKBF-W2HMG-DBMJC-PGWR7 Access 2013 NG2JY-H4JBT-HQXYP-78QH9-4JM2D Excel 2013 VGPNG-Y7HQW-9RHP7-TKPV3-BG7GB InfoPath 2013 DKT8B-N7VXH-D963P-Q4PHY-F8894 Lync 2013 2MG3G-3BNTT-3MFW9-KDQW3-TCK7R OneNote 2013 TGN6P-8MMBC-37P2F-XHXXK-P34VW Outlook 2013 QPN8Q-BJBTJ-334K3-93TGY-2PMBT PowerPoint 2013 4NT99-8RJFH-Q2VDH-KYG2C-4RD4F Publisher 2013 PN2WF-29XG2-T9HJ7-JQPJR-FCXK4 Word 2013 6Q7VD-NX8JD-WJ2VH-88V73-4GBJ7 Office Professional Plus 2016 XQNVK-8JYDB-WJ9W3-YJ8YR-WFG99 Office Standard 2016 JNRGM-WHDWX-FJJG3-K47QV-DRTFM Project Professional 2016 YG9NW-3K39V-2T3HJ-93F3Q-G83KT Project Standard 2016 GNFHQ-F6YQM-KQDGJ-327XX-KQBVC Visio Professional 2016 PD3PC-RHNGV-FXJ29-8JK7D-RJRJK Visio Standard 2016 7WHWN-4T7MP-G96JF-G33KR-W8GF4 Access 2016 GNH9Y-D2J4T-FJHGG-QRVH7-QPFDW Excel 2016 9C2PK-NWTVB-JMPW8-BFT28-7FTBF OneNote 2016 DR92N-9HTF2-97XKM-XW2WJ-XW3J6 Outlook 2016 R69KK-NTPKF-7M3Q4-QYBHW-6MT9B PowerPoint 2016 J7MQP-HNJ4Y-WJ7YM-PFYGF-BY6C6 Publisher 2016 F47MM-N3XJP-TQXJ9-BP99D-8K837 Skype for Business 2016 869NQ-FJ69K-466HW-QYCP2-DDBV6 Word 2016 WXY84-JN2Q9-RBCCQ-3Q3J3-3PFJ6 Windows: Windows 10 W269N-WFGWX-YVC9B-4J6C9-T83GX Windows 8.1 Professional GCRJD-8NW9H-F2CDX-CCM8D-9D6T9 Windows 8.1 Professional N HMCNV-VVBFX-7HMBH-CTY9B-B4FXY Windows 8.1 Enterprise MHF9N-XY6XB-WVXMC-BTDCT-MKKG7 Windows 8.1 Enterprise N TT4HM-HN7YT-62K67-RGRQJ-JFFXW Windows Server 2012 R2 Server Standard D2N9P-3P6X9-2R39C-7RTCD-MDVJX Windows Server 2012 R2 Datacenter W3GGN-FT8W3-Y4M27-J84CP-Q3VJ9 Windows Server 2012 R2 Essentials KNC87-3J2TX-XB4WP-VCPJV-M4FWM More Windows: Windows 8 Professional NG4HW-VH26C-733KW-K6F98-J8CK4 Windows 8 Professional N XCVCF-2NXM9-723PB-MHCB7-2RYQQ Windows 8 Enterprise 32JNW-9KQ84-P47T8-D8GGY-CWCK7 Windows 8 Enterprise N JMNMF-RHW7P-DMY6X-RF3DR-X2BQT Windows Server 2012 BN3D2-R7TKB-3YPBD-8DRP2-27GG4 Windows Server 2012 N 8N2M2-HWPGY-7PGT9-HGDD8-GVGGY Windows Server 2012 Single Language 2WN2H-YGCQR-KFX6K-CD6TF-84YXQ Windows Server 2012 Country Specific 4K36P-JN4VD-GDC6V-KDT89-DYFKP Windows Server 2012 Server Standard XC9B7-NBPP2-83J2H-RHMBY-92BT4 Windows Server 2012 MultiPoint Standard HM7DN-YVMH3-46JC3-XYTG7-CYQJJ Windows Server 2012 MultiPoint Premium XNH6W-2V9GX-RGJ4K-Y8X6F-QGJ2G Windows Server 2012 Datacenter 48HP8-DN98B-MYWDG-T2DCC-8W83P Older versions: Windows 7 Professional FJ82H-XT6CR-J8D7P-XQJJ2-GPDD4 Windows 7 Professional N MRPKT-YTG23-K7D7T-X2JMM-QY7MG Windows 7 Professional E W82YF-2Q76Y-63HXB-FGJG9-GF7QX Windows 7 Enterprise 33PXH-7Y6KF-2VJC9-XBBR8-HVTHH Windows 7 Enterprise N YDRBP-3D83W-TY26F-D46B2-XCKRJ Windows 7 Enterprise E C29WB-22CC8-VJ326-GHFJW-H9DH4 Windows Server 2008 R2 Web 6TPJF-RBVHG-WBW2R-86QPH-6RTM4 Windows Server 2008 R2 HPC edition TT8MH-CG224-D3D7Q-498W2-9QCTX Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard YC6KT-GKW9T-YTKYR-T4X34-R7VHC Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise 489J6-VHDMP-X63PK-3K798-CPX3Y Windows Server 2008 R2 Datacenter 74YFP-3QFB3-KQT8W-PMXWJ-7M648 Windows Server 2008 R2 for Itanium-based Systems GT63C-RJFQ3-4GMB6-BRFB9-CB83V Still even older ones: Windows Vista Business YFKBB-PQJJV-G996G-VWGXY-2V3X8 Windows Vista Business N HMBQG-8H2RH-C77VX-27R82-VMQBT Windows Vista Enterprise VKK3X-68KWM-X2YGT-QR4M6-4BWMV Windows Vista Enterprise N VTC42-BM838-43QHV-84HX6-XJXKV Windows Web Server 2008 WYR28-R7TFJ-3X2YQ-YCY4H-M249D Windows Server 2008 Standard TM24T-X9RMF-VWXK6-X8JC9-BFGM2 Windows Server 2008 Standard without Hyper-V W7VD6-7JFBR-RX26B-YKQ3Y-6FFFJ Windows Server 2008 Enterprise YQGMW-MPWTJ-34KDK-48M3W-X4Q6V Windows Server 2008 Enterprise without Hyper-V 39BXF-X8Q23-P2WWT-38T2F-G3FPG Windows Server 2008 HPC RCTX3-KWVHP-BR6TB-RB6DM-6X7HP Windows Server 2008 Datacenter 7M67G-PC374-GR742-YH8V4-TCBY3 Windows Server 2008 Datacenter without Hyper-V 22XQ2-VRXRG-P8D42-K34TD-G3QQC Windows Server 2008 for Itanium-Based Systems 4DWFP-JF3DJ-B7DTH-78FJB-PDRHK
Revert windows 10 VPN connection to older type 'connect' button
Open regedit (WIN+R and type regedit.exe)
Go to
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\ControlPanel\Settings\Network
Take ownership of the “Network” key/folder (rightclick, Permissions)
Select “Advanced” in the Permissions window In the Advanced window,
select “Change” where the owner field is (top of the window)
Type in your username and save your changes. Close the advanced window.
Now select “Administrators” in the security tab. Make sure “Full control” is selected, then apply changes.
Now that’s done, double click “ReplaceVan” Change it’s value to 2
Certificates
Check key / cert are mached (also csr )
checking the modulus and the public exponent portions in the key and the Certificate must match.
But since the public exponent is usually 65537 and it's bothering comparing long modulus you can use the following approach:
$ openssl x509 -noout -modulus -in server.crt | openssl md5 $ openssl rsa -noout -modulus -in server.key | openssl md5
And then compare these really shorter numbers.
if I want to check to which key or certificate a particular CSR belongs you can compute
$ openssl req -noout -modulus -in server.csr | openssl md5
Re-install Grub / fix partitions
Boot from the live CD or live USB, in "Try Ubuntu" mode.
Determine the partition number of your main partition. GParted (which should already be installed, by default, on the live session) can help you here. I'm going to assume in this answer that it's /dev/sda2, but make sure you use the correct partition number for your system!
Mount your partition:
sudo mount /dev/sda2 /mnt #Replace sda2 with your partition number Bind mount some other necessary stuff:
for i in /sys /proc /run /dev; do sudo mount --bind "$i" "/mnt$i"; done
chroot into your Ubuntu install:
sudo chroot /mnt At this point, you're in your install, not the live session, and running as root. Update grub:
update-grub If you get errors, go to step 7. (Otherwise, it is optional.)
Electronics Related
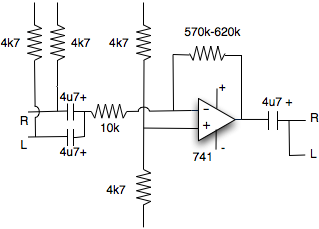
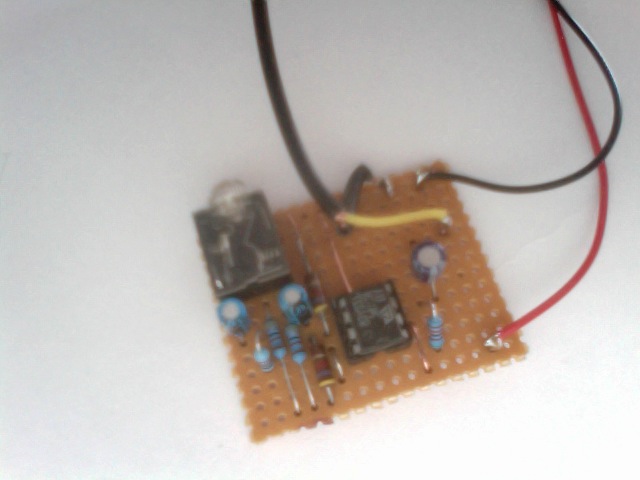
Microphone pre-amp for apple mac
This simple circuit was built on vero board in a matter of 40 mins. Not pretty but it was made of mostly second hand bits, infact two of the resistors bellow where from a PC board from a 1980's computer!
Arduino Atmega8 using internal 8mhz clock
How to add atmiga8 chip to the IDE interface for Arduino, this is for the old version 1.0.6. I've never bothered using the later versions but I would think is mostly the same
Change to the optiboot directory (this is on the Mac OS X version, for windows just look for the bootloaders directory
cd /Applications/Arduino.app/Contents/Resources/Java/hardware/arduino/bootloaders/optiboot/
Add this to the Makefile, I would suggest just after the existing atemga8 section, I used the letter i to indicate internal clock
atmega8i: TARGET = atmega8 atmega8i: MCU_TARGET = atmega8 atmega8i: CFLAGS += '-DLED_START_FLASHES=3' '-DBAUD_RATE=38400' atmega8i: LDSECTIONS = -Wl,--section-start=.text=0x1e00 -Wl,--section-start=.version=0x1ffe atmega8i: AVR_FREQ = 8000000L atmega8i: $(PROGRAM)_atmega8i.hex atmega8i: $(PROGRAM)_atmega8i.lst atmega8i_isp: atmega8i atmega8i_isp: TARGET = atmega8 # 2.7V brownout atmega8i_isp: HFUSE = CC # internal clock 8mhz atmega8i_isp: LFUSE = A4 # 512 byte boot atmega8i_isp: EFUSE = 04 atmega8i_isp: isp
You can then make the boot loader with the omake command (on the Mac you have to chmod +x omake first)
./omake atmega8i
(you will end up with a " optiboot_atmega8i.hex ") file in the directory,
Next add these lines to the boards.txt file (normally at the bottom of the file)
This adds two entries to your board selection the first 8-16MHZ is for Crystal clock, the second (8mhz) is the internal clock version at 8mhz. You can change the fuse bits to get other clock speeds if you need them.
############################################################## opti8.name=Arduino Optiboot-Atmega8-16 opti8.upload.protocol=arduino opti8.upload.maximum_size=7680 opti8.upload.speed=115200 opti8.bootloader.low_fuses=0xbf opti8.bootloader.high_fuses=0xcc opti8.bootloader.path=optiboot #opti8.bootloader.file=optiboot_atmega8-16.hex opti8.bootloader.file=optiboot_atmega8.hex opti8.bootloader.unlock_bits=0x3F opti8.bootloader.lock_bits=0x0F opti8.build.mcu=atmega8 opti8.build.f_cpu=16000000L opti8.build.core=arduino opti8.build.variant=standard ############################################################## ############################################################## opti8i.name=Arduino Optiboot-Atmega8-16 (8mhz) opti8i.upload.protocol=arduino opti8i.upload.maximum_size=7680 opti8i.upload.speed=38400 opti8i.bootloader.low_fuses=0xa4 opti8i.bootloader.high_fuses=0xcc opti8i.bootloader.path=optiboot opti8i.bootloader.file=optiboot_atmega8i.hex opti8i.bootloader.unlock_bits=0x3F opti8i.bootloader.lock_bits=0x0F opti8i.build.mcu=atmega8 opti8i.build.f_cpu=8000000L opti8i.build.core=arduino opti8i.build.variant=standard ############################################################## </pree>